Zero to Hero: Singapore’s Economic Transformation
Can India replicate this?
Story of X and Y
Imagine country X plagued by poverty, unemployment, drug addiction, riots, and illiteracy.
Now imagine another country Y, as one of the world's most developed and richest nations, admired for its cleanliness, low corruption, and harmonious society.
Think X and Y are poles apart?
Think no more! Because X is Singapore in 1965 and Y is Singapore again but in today’s time.
Located at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, Singapore is a densely populated country. It is a country so small that it is half the size of Delhi! It harbours over 5.7 million people of diverse ethnicities and religions.
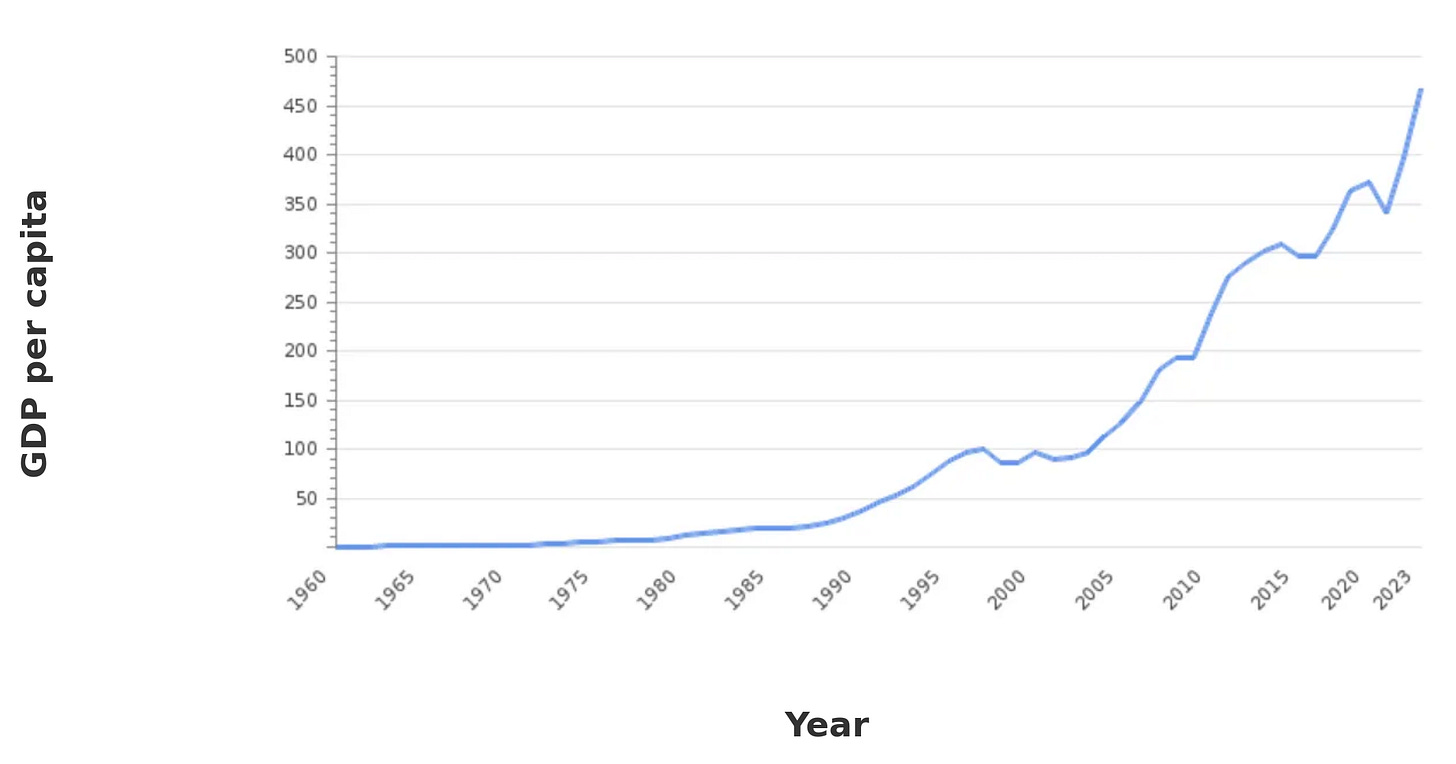
Much to global curiosity, it transitioned from a resource-poor nation with per capita GDP of $516 to an export-heavy nation with per capita GDP risen to over $82,000, ranking itself among the highest globally.
But how did this small island nation achieve such a dramatic turnaround?
Let's start from the start! Once a humble fishing village, Singapore attracted global interest due to its strategic location at the crossroads of major maritime trade routes. It connects the Indian Ocean to the South China Sea and Pacific Ocean and is close to the Strait of Malacca, one of the world’s busiest shipping lanes through which much of the global trade flows.
In 1819 under the British rule, Sir Stamford Raffles of the British East India Company turned Singapore into a free port, making it a key hub for global trade for Asia and beyond. Under the Japanese occupation of Singapore in 1942, the island's residents were plunged into a nightmare of hardship and fear. Food became scarce. Many were forced into labor camps, where they toiled under brutal conditions, while others lived in constant fear of persecution and violence.
Economy Unveiled aims to present heavily researched yet easily digestible financial content! We write about the biggest stories in the markets to help you understand what they mean for you and the world.
Wonder why read us? We are a team of researchers, CAs, and CFA professionals committed to leveraging the power of research to provide valuable content for our daily readers.
Explore our products here and chat with us on Whatsapp for more. Subscribe to our newsletter and stay connected!
Japan's rule ended soon in 1945, but what remained back was a dark legacy of poverty, unemployment, crime, and ethnic tensions with a significant part of the population turned into drug addicts and criminals. In 1959, Singapore gained partial self-governance, with Lee Kuan Yew as its first Prime Minister who took on the herculean task of pulling the nation out of this abyss for a remarkable transformation.
The challenge was daunting! But what happened after this is equally shocking!
The graph below illustrates the exponential growth of Singapore's GDP growth over time. In 2024, Singapore's economy experienced a significant growth of 4.0%, marking its fastest annual expansion since the pandemic recovery.
"The Impossible Can Happen!"
In a press conference, referring to the airline pilot strike of Singapore Air, Lee Kuan Yew (also called as the founding father of Singapore) said:
"I have spent a lifetime building this (Singapore), and as long as I am in charge, no one is going to knock it down.”
I have added this statement here because it truly reflects on Yew’s legendary leadership and commitment to transform Singapore.
Leaders, economists, and institutions across the world have acknowledged his visionary strategies which I will categorize into four core verticals: Infrastructure and Industries, Policies and Investments, Governance, and Sustainability and Social Development.
Infrastructure and Industries
Export! Export! Export!
Singapore transitioned from import substitution to export-driven industrialization, positioning itself as a global trading hub. Leveraging its strategic location, the government attracted multinational corporations (MNCs) and laid the groundwork for high-value industries like electronics, petrochemicals, and pharmaceuticals. This focus on exports not only diversified the economy but also cemented Singapore’s role in global trade.
Too fin to know! Studies show that African firms, when they focus on exports, see faster productivity growth. For instance, Kenya’s fresh produce exports like flowers and nuts, despite high logistics costs, have created jobs and increased incomes.
Cool, right? What are your thoughts on this?
Diversification and beyond!
Low-cost manufacturing is an effective starting point for industrialization but to remain competitive and achieve sustained growth, economies must transition toward high-value industries because rising wages and global competition erode the cost advantage of low-cost manufacturing over time.
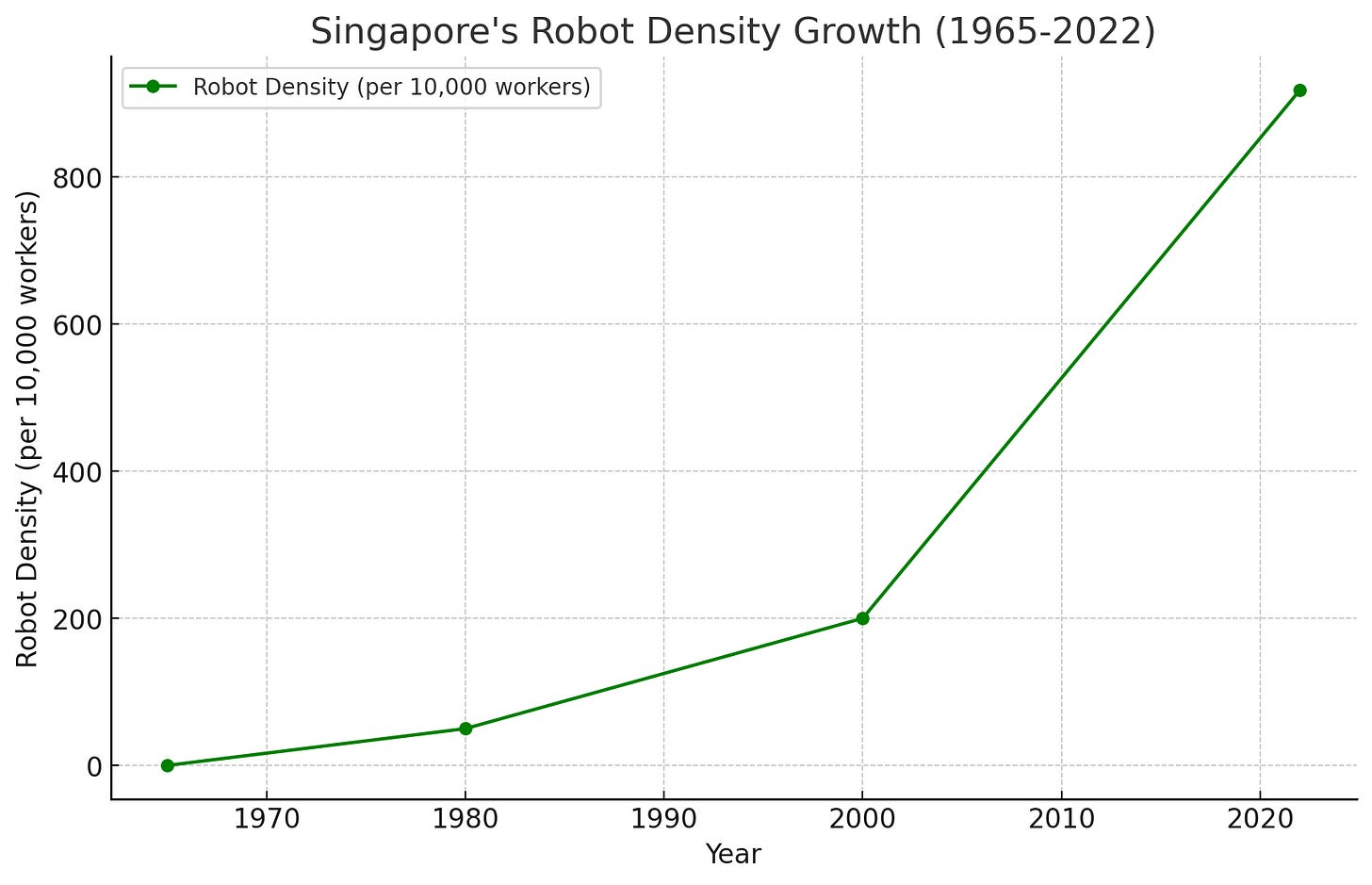
Recognizing this limitations, Singapore diversified towards advanced industries such as semiconductors, biotech, aerospace, and pharmaceuticals. Today, it uses a robot workforce to perform many tasks traditionally done by humans. While specific projections for 2025 are not readily available, as of 2023, Singapore ranks as the second most robot-dense country globally, with approximately 770 industrial robots per 10,000 employees.
Singapore now ranks second only to South Korea in robot density!
Infra and build!
Yew’s government prioritized world-class infrastructure, including state-of-the-art ports, airports, and industrial parks, to support manufacturing and trade. The creation of industrial parks through the Economic Development Board (EDB) further enhanced Singapore’s appeal as a manufacturing and logistics hub.
Policies and Investments
Welcome FDIs!
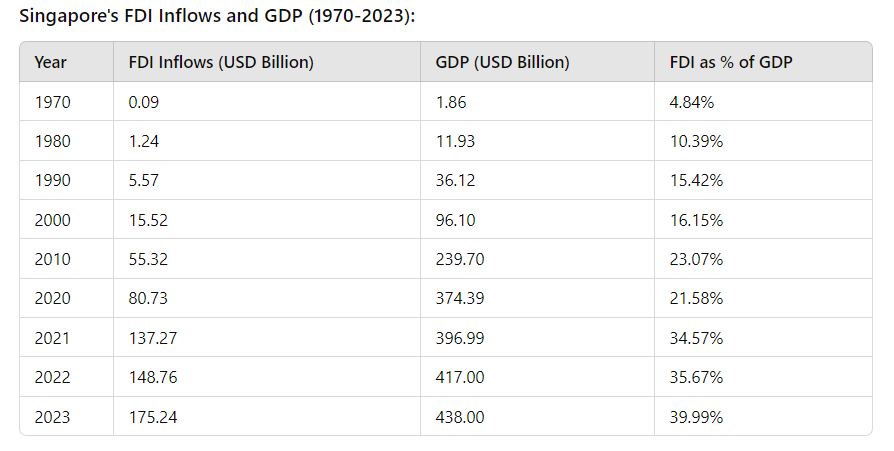
Singapore’s government actively created a business-friendly ecosystem by reducing taxes, cutting bureaucratic red tape, and ensuring political stability. The establishment of the Economic Development Board (EDB) in 1961 played a pivotal role in attracting foreign investors. The EDB incentivized MNCs with tax breaks, streamlined regulations, and industrial zones, transforming Singapore into a prime investment destination.
Check out the table below to fulfill your craving for stats!
Fin-bits! MNCs are the lifeblood of FDI, bringing capital, expertise, and global connectivity to host countries. FDI, in turn, provides MNCs with opportunities for expansion, cost optimization, and market access.
This symbiotic relationship drives globalization and economic integration, but host countries must balance the benefits of FDI with the risks of over-reliance on MNCs like Singapore did to achieve long-term sustainability!
Now, it's your turn to leverage this formula by investing in a portfolio designed to capture the growth potential of emerging global giants. Click here to invest in Emerging Global Giants - Global Companies.
Public-Private collab!
Collaboration between the government and private sector was critical to Singapore's growth. Sovereign wealth funds like Temasek Holdings were established to manage investments and ensure fiscal sustainability. Programs like the Industry Transformation Programme (ITP) encouraged public-private partnerships, fostering innovation and industry-specific strategies that addressed long-term economic goals.
Governance and Anti-Corruption
Trust the state!
Singapore built a global reputation for transparency and clean governance. The establishment of the Corrupt Practices Investigation Bureau (CPIB) ensured independent investigations into corruption. Yew introduced competitive salaries for public officials to discourage bribery and promote integrity in governance.
Transparent and efficient governance became the backbone of Singapore as a nation. Policies were implemented with accountability and a long-term vision, aligning public administration with economic goals.
Sustainability and Social Development
Stable so stable!
The government promoted financial sustainability through initiatives like the Central Provident Fund (CPF), which encouraged savings and ensured long-term stability for citizens. Sovereign wealth funds such as Temasek Holdings generated revenue through strategic investments, reducing reliance on taxation.
The will to Skill!
As a critical step to rejuvenate and empower a population that had endured the trauma during Chinese rule, education and skill development were central to Singapore's growth. Compulsory education, coupled with initiatives like SkillsFuture, emphasized vocational training and lifelong learning. This focus on human capital prepared the workforce for the demands of modern industries, ensuring continued economic resilience and adaptability.
Fin fact! Did you know that Singapore's passport is one of the most powerful in the world, allowing its citizens visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to a wide range of countries. This highlights the nation's emphasis on fostering global connectivity and ease of travel for its citizens.
Combating Premature Deindustrialisation
Imagine a ladder to abundancy having three big steps:
FARMING (growing food, raw material)
FACTORIES (making things like clothes and cars)
SERVICES (teaching, designing apps, or running shops)
In your village, the plan is to climb this ladder to become rich and have everything you need: starting with farming, then building factories to make cool things, and finally focusing on creative jobs like inventing or selling products.
But here’s the catch! Other villages build factories faster and produce goods more cheaply, so instead of creating your own factories, you just buy from them. Then, super-smart robots came along, and factories no longer need as many workers. Before you can even get halfway up the ladder, the factories, you are left unable to climb higher.
Popularized by economist Dani Rodrik in 2015, this is what economists call ‘Premature Deindustrialization’: In simple words, you lose the chance to grow through factories because you're either outcompeted by others or replaced by robots.
There has been a well-noted trend of developed countries where they outsource their manufacturing to lower-wage nations. Companies like Zara, H&M, Samsung, Hyundai, IKEA, Accenture, and Amazon have leveraged this trend by either sourcing their products or setting up production facilities in countries like China, India, Vietnam, and Bangladesh, where labor is cheaper.
Developing countries are expected to rely on manufacturing as a key driver for economic growth and employment during their industrialization phase. But on the other hand, they are unable to compete with established manufacturing hubs with advanced automation and low-cost manufacturing. They end up experiencing a decline in manufacturing before they become wealthy or achieve high-income status.
But Singapore stands as an outlier amongst other struggling developing nations (including India)!
It reversed its decline in manufacturing through strategic policies and heavy automation by working on its core manufacturing capabilities and investment strategies as discussed earlier!
The Wall Street Journal (one of the most prominent financial newspapers worldwide and winner of a number of Pulitzer Prizes!) highlights how Singapore reversed the decline in manufacturing's share of GDP, which fell from 27% in 2005 to 18% by 2013, by increasing it to 21% in 2020 and 22% in 2022 through heavy automation.
Singapore also attracted highly automated factories by offering research partnerships, subsidized training, and grants to local manufacturers.
Imagine if you were an employee at a Singapore factory and these would be your friends at work.
For example, At Siemens' fully digitalized plant in Singapore, AI-powered systems, autonomous vehicles, and collaborative robots work alongside humans, making it an innovation hub for Industry 4.0 (The Fourth Industrial Revolution!)- an entire factory where robots build other robots!
Can India be the Copy-cat?
India ain’t. India can’t.
India can draw significant lessons from Singapore’s economic model, but replicating it entirely is a path that must be tread carefully due to differences in scale, demographics, and socio-economic conditions.
Infrastructure and investments
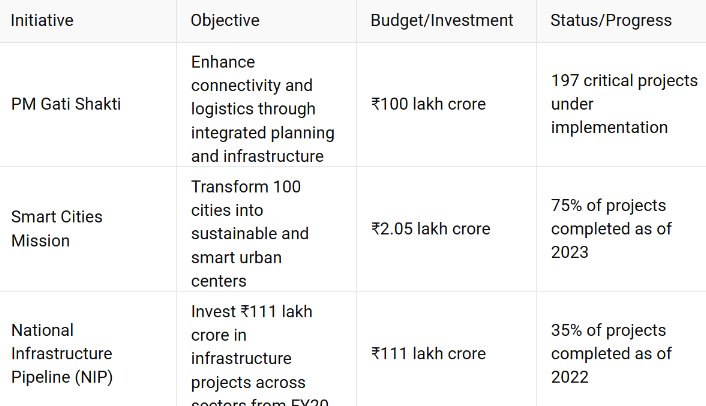
As discussed, Singapore’s seamless ports, public transport, and urban planning have played a pivotal role in attracting global investors. India, through initiatives like PM Gati Shakti, Smart Cities Mission, and the National Infrastructure Pipeline (NIP), is already working towards enhancing connectivity, logistics, and urban development. However, addressing bureaucratic inefficiencies and improving the speed of project execution remain critical challenges.
A recent example for this is Tata Power's 100-megawatt solar plant project in Maharashtra's Nandgaon due to land disputes with local farmers. Protests and legal challenges prompted the Maharashtra forest department to temporarily halt the project.
As Singapore’s success lies in blending high-tech automation with a highly skilled workforce. India can adopt a similar dual approach by fostering advanced manufacturing hubs through initiatives like Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Schemes and supporting labor-intensive sectors such as textiles and food processing.
Programs like Skill India and Digital India are equipping the Indian workforce with modern skills, but further investments in vocational training and STEM education are essential to meet the demands of Industry 4.0 while creating inclusive job opportunities.
In the headlines! India and Singapore are making headlines as they join forces to develop a robust semiconductor ecosystem, reflecting their shared commitment to advancing technological capabilities and achieving economic resilience.
Governance and sustainability
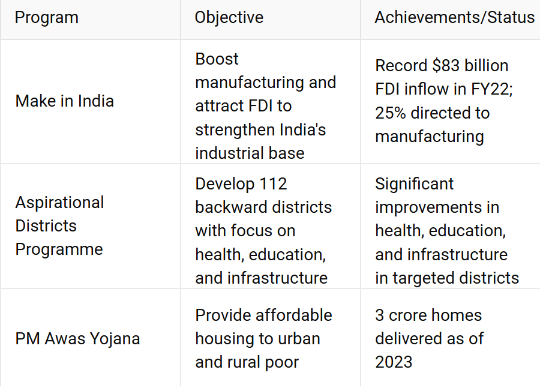
Singapore’s small size allowed it to evenly distribute economic gains, whereas India faces significant challenges in bridging the gap between urban and rural regions. Initiatives like Make in India, Aspirational Districts Programme, and PM Awas Yojana aim to address these inequalities by driving rural development, creating job opportunities, and improving access to basic amenities.
India must also ensure that high-tech automation does not widen the urban-rural divide and instead focus on integrating advanced manufacturing with small-scale industries in rural areas to promote balanced growth.
Initiatives like One District, One Product (ODOP) should be encouraged for rural areas to incentivise unique small-scale industries while integrating technology as well. For instance, Uttar Pradesh has supported rural artisans in Varanasi's silk weaving industry by providing advanced looms and digital marketing platforms.
This approach integrates modern technology with traditional craftsmanship, helping rural industries compete globally and fostering balanced growth without exacerbating the urban-rural divide!
But the times are changing..
The global economic landscape has been undergoing significant shifts in recent years, with many nations turning towards protectionist policies and self-reliance. This adds further complexity to the already challenging question of adopting Singapore’s strategy.
The Trump administration in the United States marked a notable pivot with its "America First" strategy, emphasizing reduced imports, reshoring manufacturing, and imposing tariffs on goods from countries like China. This trend of ‘economic nationalism’ has influenced other nations, pushing them to adopt similar self-reliant measures. For instance, China has ramped up its domestic production capacities under its "Dual Circulation Strategy" to focus on internal consumption while maintaining global trade competitiveness.
Additionally, the Russia-Ukraine conflict has disrupted global supply chains, particularly for energy and agricultural products, highlighting the vulnerabilities of over-dependence on specific regions for essential goods. Bangladesh, too, has capitalized on this global shift by boosting its textile exports, while India has seen opportunities to position itself as a manufacturing hub through initiatives like Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India).
For India, these geopolitical shifts underline the importance of building a robust domestic manufacturing ecosystem while also strategically engaging with global trade partners at the same time.
While you wait for that transformation…
Don’t wait to subscribe to Economy Unveiled - stay ahead and be the first to know the best!
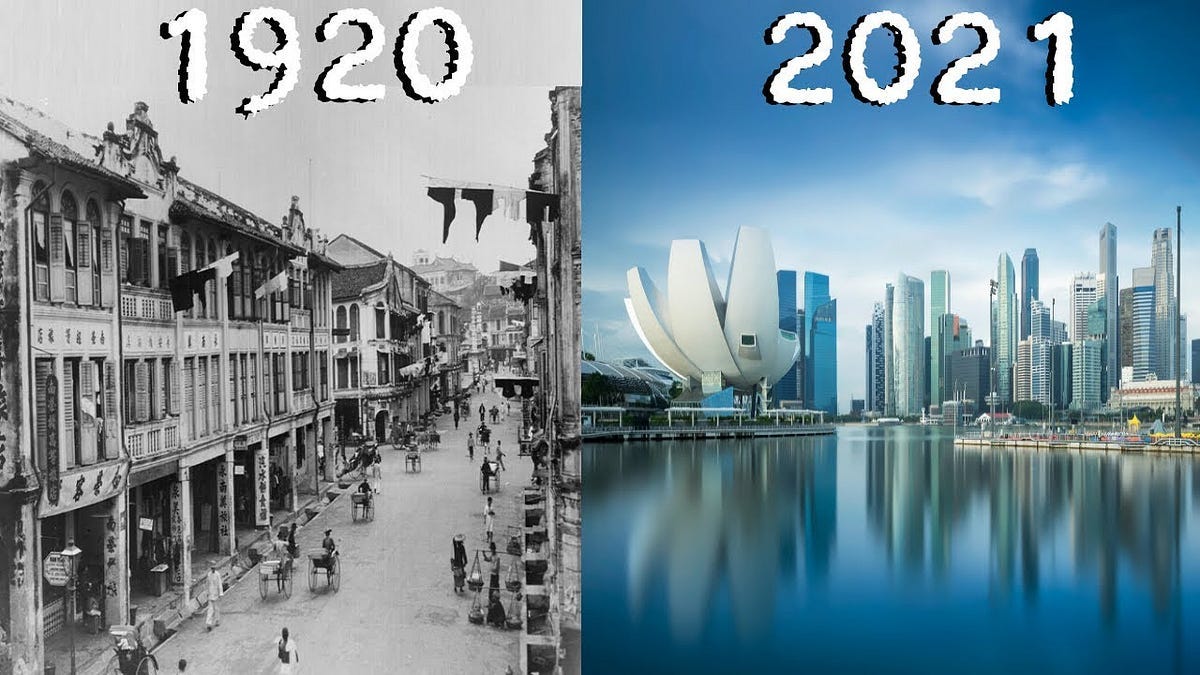





A great reminder of how determination and smart policies can turn a nation’s fate around
Well-written and insightful!
It was nice getting this historical context :)